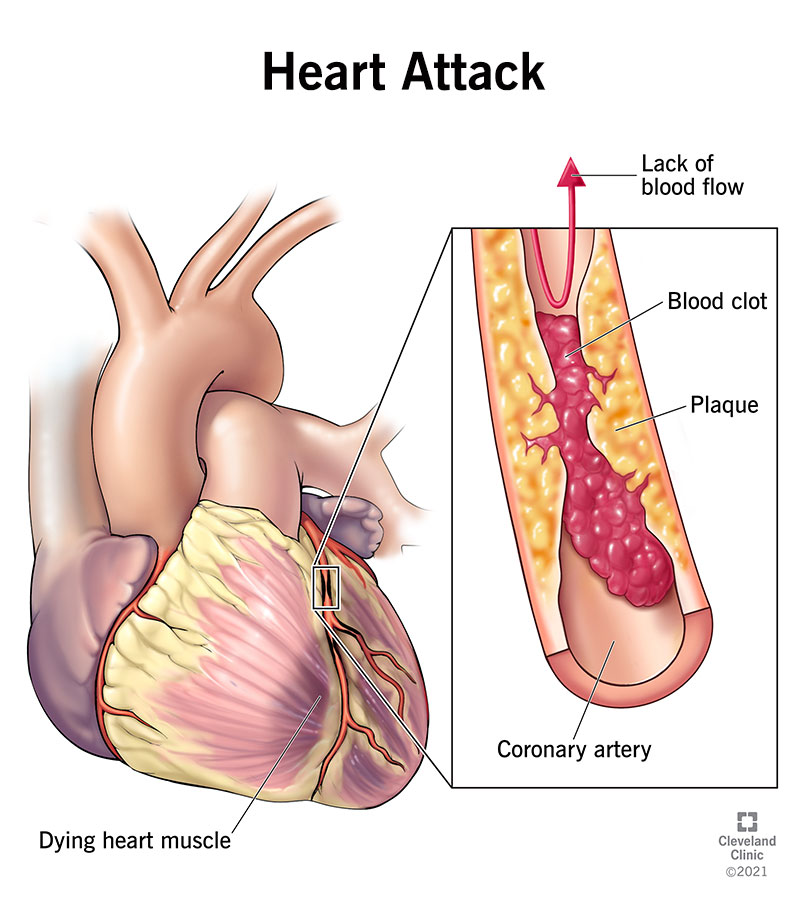
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can cause damage to the heart muscle. While a defibrillator cannot treat a heart attack itself, it can be used in conjunction with other interventions to help save a person's life if they experience sudden cardiac arrest as a result of a heart attack or another cause.
















0 Comments:
Post a Comment